What are Anti-static and ESD?
The term electrostatic dissipation (sometimes referred to as electrostatic discharge) refers to the dissipation of static electricity. Anti-static, on the other hand, is more self-explanatory.
It is important to understand that ESD and anti-static are not the same thing, which can cause confusion when searching for the best safety footwear.
Anti-static and ESD safety shoes are both conductive, which means they protect electrical equipment by conducting electrical charges to the ground so that static shock, charge, and sparks are prevented.
The use of conductive safety footwear is essential for industries where static shock could damage electronic equipment or even increase the risk of fires and explosions. In contrast, isolating safety shoes (EH-rated) prevent you from completing an electrical circuit to the ground. There is a potential danger in confusing the two!
Despite the fact that both antistatic and ESD refer to contact resistance, there are fundamental differences between the two:
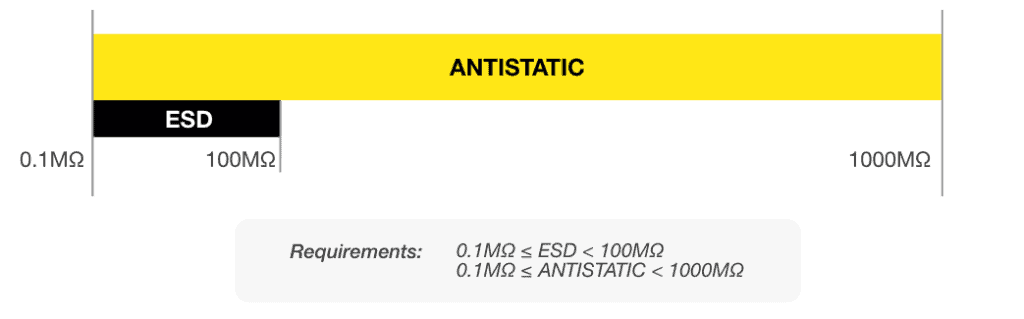
Antistatic footwear has a low electrical resistance between 0.1 and 1000 MegaOhm (MΩ). By sending static electrical charges to the ground, anti-static footwear prevents the accumulation of static electrical charges in the human body. In this way, electrical charges are prevented from flowing suddenly between electrically charged objects when they come in contact. As a result, static shock can be reduced when touching metal equipment, such as hospital beds for example.
ESD (Electrostatic Dissipation/ Discharge) footwear, on the other hand, has a much lower electrical resistance of between 0.1 and 100 MegaOhm (MΩ). Through the use of ESD occupational and safety footwear, static electrical charges are sent to the ground in a controlled and safe manner. As a result, they prevent electrical currents from flowing between electrically charged objects when they come into contact.
ANTISTATIC
Antistatic safety shoes reduce the chance of electrostatic discharges.
Electrical resistance between 0.1 and 1000 (MΩ)
Norm – EN 20344: 2011 5 10
Sufficient dissipative capacity
100% Tested in production
ESD
ESD safety shoes prevent uncontrolled electrostatic discharges.
Electrical resistance between 0.1 and 100 (MΩ)
Norm – BS EN 61340-4-3: 2002 (IEC 61340-4-3:2001)
Guaranteed extremely low electrical resistance under any conditions
100% Tested in production
In a variety of industries, anti-static footwear and ESD prevent electrostatic discharges from damaging sensitive equipment and components. To name a few, they include aerospace, IT, manufacturing of semiconductors and industrial equipment, electrical engineers, telecommunications, computer manufacturing, and the medical profession.
There are a number of harmful effects on worksites that can be prevented by ESD. Gas, fuel vapour, and coal dust explosions can be caused by the uncontrolled release of static charges. Solid-state electronic components, such as integrated circuits, can also be damaged. ESD safety or occupational footwear is therefore essential for people who work in these environments.
ESD Classes
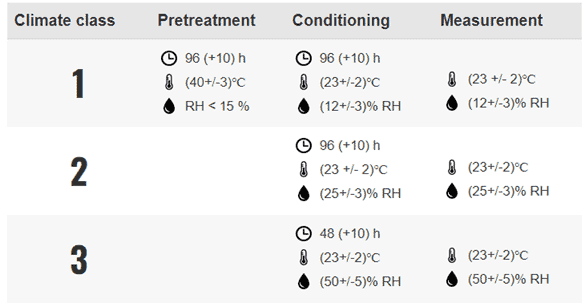
A shoe’s electrical resistance is greatly affected by temperature and humidity (including moisture content in the footwear). Safety and occupational footwear with ESD protection comes in three climate classes: 1, 2 & 3.
Time of conditioning, temperature, and humidity differ between these three classes. For example, climate class 1 has the highest temperature and lowest humidity of all ESD classes. When safety shoes satisfy the class 1 criteria (an electrical resistance between 0.1 and 100 MΩ) they have a guaranteed low electrical resistance, even under exceptional circumstances.
A laboratory test method is used to test the ESD properties of safety shoes for ESD certification. A stainless-steel plate is used as the first electrode, and a counter electrode is placed inside the safety shoe on the insole. Weight of 12.5 kg (+/- 2.5 kg) is then applied. The contact resistance between two electrodes is measured by a device. For ESD certification to be granted for the respective climate class, the resistance must be less than 100 megaohms.
ESD Technologies
There are 3 main ways in which Safety Jogger and Oxypas apply ESD technology to professional footwear:
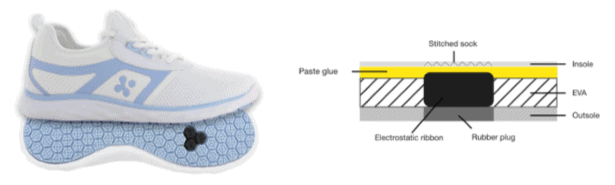
Sock Stitched + PU

Sock Stitched + ESD Plug
EVA + ESD Plug
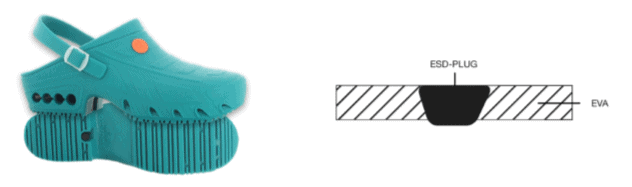
EVA (Ethylene-vinyl Acetate) is the material used in many of our washable styles for industries such as medical, catering, food production, laboratories and any clean environments where this type of footwear would be beneficial. Today, many styles of shoe, including trainers, use this material in the midsole.
Would you like to learn more about professional footwear before making a decision? Here are some blog articles you may find helpful:
What are slip-resistance standards? Click here to read our ‘Slips, Trips and Falls – Slip Resistance Explained’ blog.
What are slip-resistance standards? Click here to read our ‘Safety and Occupational Footwear Explained’ blog.
Looking for student placement shoes? Click here to read our ‘Best Shoes for Student Nursing Placement’ blog.
Do you have Plantar Fasciitis or other common aches and pains? Click here to read our ‘The Best Shoes for Plantar Fasciitis’ blog.
Looking for washable footwear? Click here to read our ‘Washable Shoes and Clogs for Nurses’ blog.
Do you have sore or tired feet? Click here to read our ‘5 Top Tips for Happy Healthy Feet’ blog.
What are the best nursing shoes for you? Click here to read our ‘The Best Nursing Shoes’ blog.



